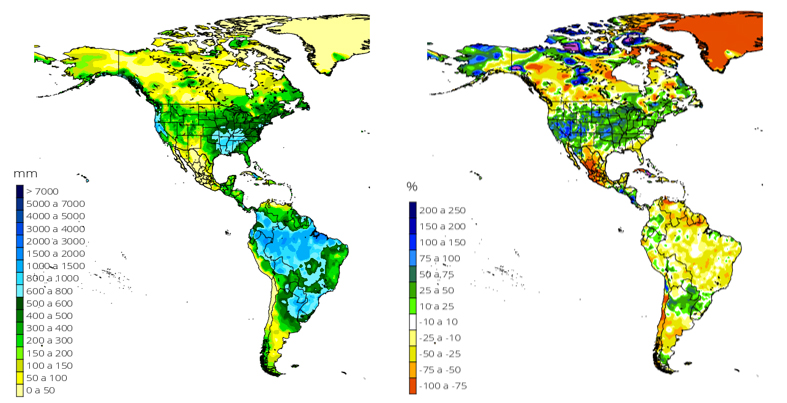
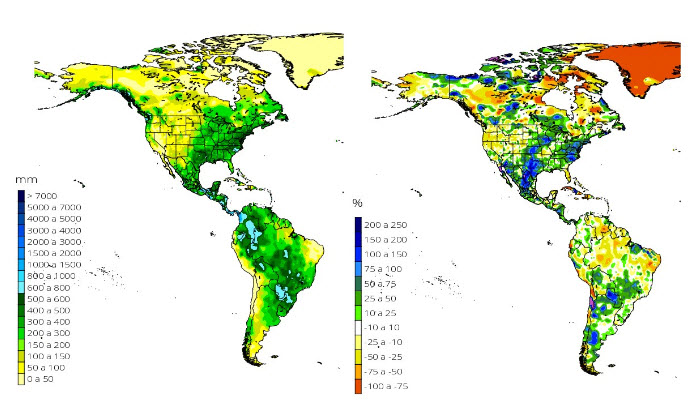
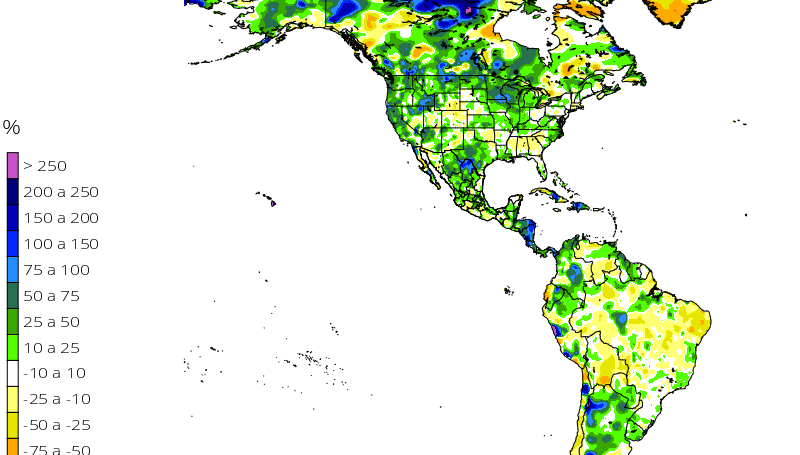
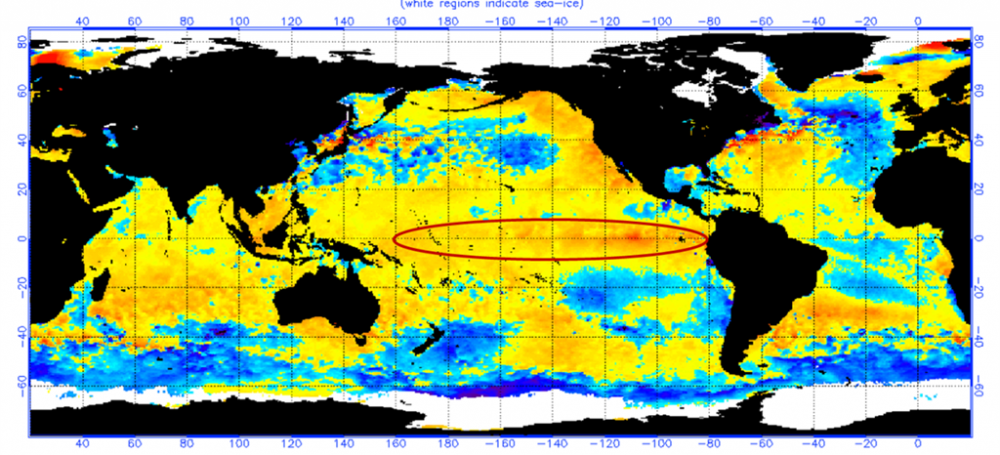
The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon started from mid-2018 and ended in June 2019, the intensity was from a weak to moderate El Niño condition. The Tropical Pacific temperature anomaly in the ENSO 3.4 region reached a maximum value of 1.3 ° C. In July it is declared again as a neutral phase.
During September and beginnings of October, surface temperature anomaly values of the Tropical Pacific that had remained around 0.5°C grew steadily up to 1.1°C above the average at the beginning of December, thus leading to El Niño 2019 if it remains along 3 consecutive months.
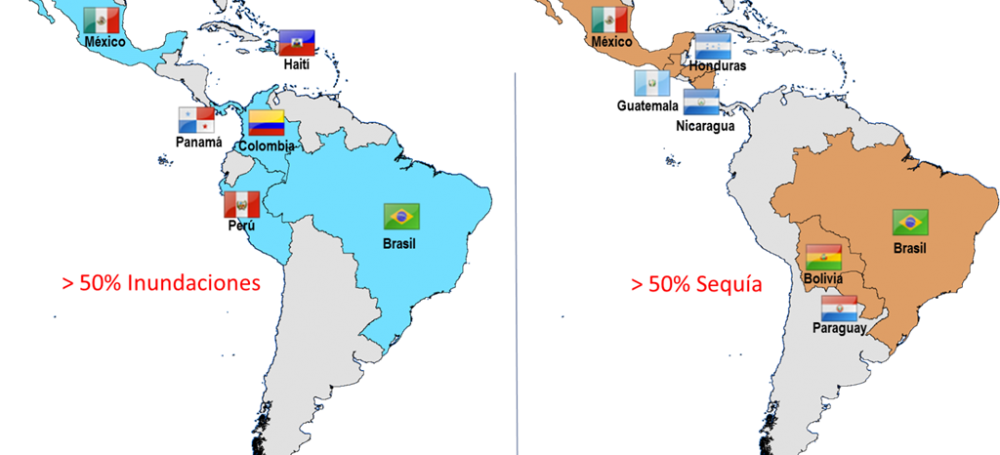
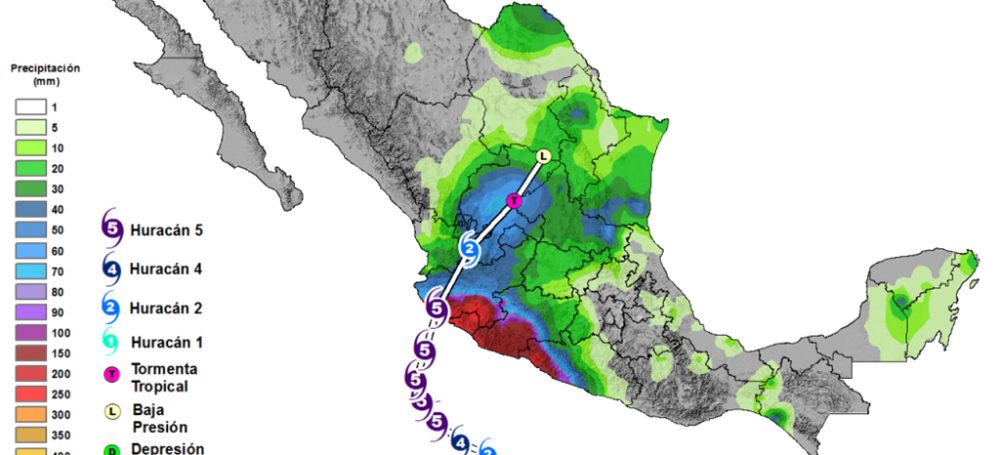
This is the count of the impacts of meteorological and climatic events in the Americas (Chart 1). In large regions of North America there was above-average rainfall during the September-November quarter in Central and Eastern Canada,
During the first semester, climate in the Americas had the influence of the event El Niño which began in 2014 and finished on May, 2016, followed by the condition Neutral. Its effects were felt in some areas of the North, Center and South America. Those were deep droughts together with sectional flooding produced by intense rainfall. However, it can be said that 2016 was a year of good weather in general terms. This was reflected in the increasing production of several
Even though many skeptics doubt about the existence of the progressive global warming due to the increasing concentration of greenhouse gasses such as, mainly, carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere; reality is that climate has changed in the last 50 years. This, considering the results of scientific researches that support that the increase of extreme climate events such as droughts, frosts, flooding, more intense hurricanes, tornados, from recent years are related to the planet temperature increase.
In the
According to the results of the forecasts of IRI, NOAA and other international institutions specialized in climate study: this summer, on the North hemisphere, and winter, in the South hemisphere, in 2015 the climate event El Niño on its Extreme condition, would cause significant changes in rainfall and temperature patterns in the American Continent. Now it’s time to count affectations in order to assimilate past events and to apply the acquired knowledge so as to benefit the crop insurance.
El Niño
Global Agricultural Insurance, including that practiced in the Americas, is a strategic response by governments to cope with the onslaught of extreme weather events resulting from Climate Change and that have a direct impact on food production. This is part of a process of adapting current agriculture to the new climatic circumstances of the world in order to mitigate the impacts of extreme events in the socio-economic environment. Crop insurance, today, is already a robust instrument commonly used among the countries